Kubernetes handles workload scaling seamlessly. This guide shows how to scale your application manually using the Kubernetes Basics tutorial. You learn to adjust replica counts, observe new pods, and maintain service availability without downtime.
TL;DR
- Deploy app with
kubectl runand expose via LoadBalancer. - Use
kubectl scale deployment <name> --replicas=Nto adjust pod count. - Watch new pods appear via
kubectl get podsorkubectl get rc/deployment. - Patches support scaling via
kubectl patchfor declarative updates. - Scaling down deletes pods gracefully; scaling up starts new pods on available nodes.
Scale Your App – Basics
Kubernetes uses declarative APIs to manage workload size. A Deployment resource exposes a scale subresource. You set spec.replicas and Kubernetes ensures the actual pod count matches. This model removes manual container orchestration.
Manual Scaling with kubectl scale
The kubectl scale command updates the replicas field on a controller or deployment. You can scale up or down instantly.
kubectl scale deployment hello-node --replicas=3Here, the Deployment named hello-node grows from its current count to three pods. Kubernetes schedules new pods across available nodes.
To scale down, set replicas lower than current count:
kubectl scale deployment hello-node --replicas=1Pod termination follows the termination grace period configured on the pod spec.
Verifying Pod Scaling
After issuing a scale command, verify with:
kubectl get podsThe output shows new pods with names suffixed by random IDs:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-node-5d8b8d5c5d-abcde 1/1 Running 0 30s
hello-node-5d8b8d5c5d-fghij 1/1 Running 0 28s
hello-node-5d8b8d5c5d-klmno 1/1 Running 0 27sYou can also inspect the Deployment resource:
kubectl get deployment hello-node -o yamlLook for status.replicas matching spec.replicas.
Scale Your App – Architecture Diagram
The diagram below shows a Service fronting a Deployment. Scaling adjusts pod count; the Service load-balances traffic across pods.
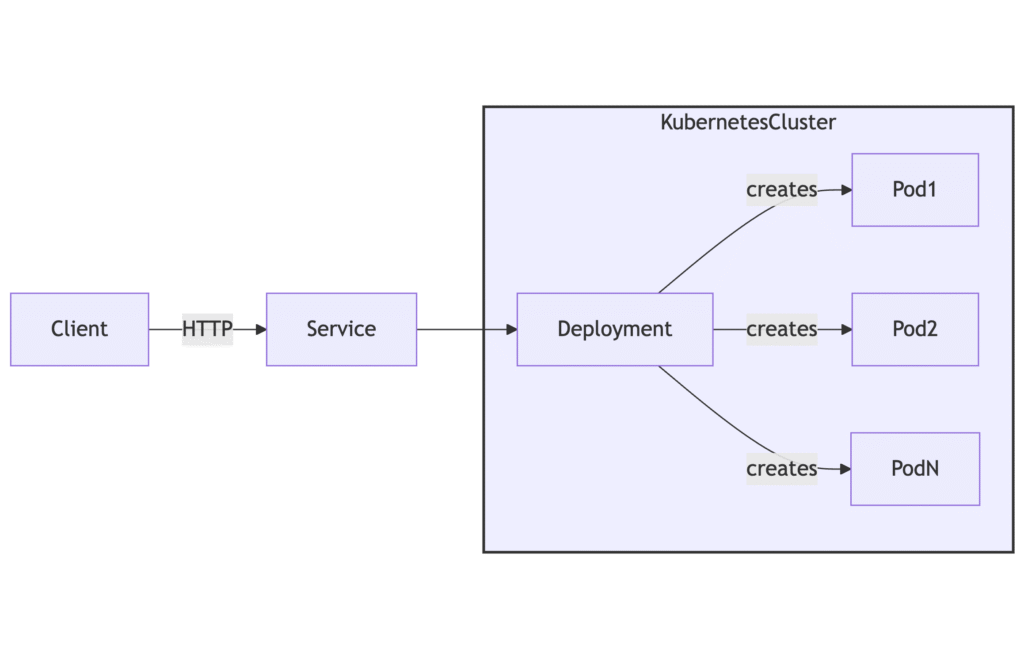
Scale Your App via Declarative Patch
You can scale declaratively using kubectl patch. This updates only the replicas field without sending the full spec:
kubectl patch deployment hello-node -p '{"spec":{"replicas":4}}'The patch merges into the live object, triggering the controller loop to adjust pods. This suits automation scripts and CI/CD workflows.
Scaling Edge Cases and Best Practices
- Avoid scaling beyond node capacity. Monitor node resources with
kubectl top nodes. - Use readiness probes to prevent traffic to pods still initializing.
- Set resource requests and limits to help the scheduler place new pods effectively.
- Combine manual scaling with autoscalers for flexible workload spikes.
References
Suggested Reading
PostHashId: f42bcef99e2e22b9a75919adee2e8e965c815e734a0f2cb44de373356b6960d9




