Rolling back a DaemonSet in Kubernetes returns your cluster to a known good state when an update fails. You can revert to a prior revision without downtime. This guide shows step-by-step commands, YAML samples, verification and troubleshooting to restore your DaemonSet in production.
TL;DR
- List DaemonSet revisions with
kubectl rollout historyto inspect past updates. - Rollback using
kubectl rollout undo daemonset/<name>or--to-revisionflag. - Verify status via
kubectl get dsandkubectl describe dsto confirm the revision number. - Use YAML patch or full spec to automate rollback in CI/CD pipelines.
- Embed a Mermaid diagram to illustrate the rollback workflow.
- Refer to troubleshooting tips if pods do not update correctly or if revision history is lost.
Understanding DaemonSet rollback
A DaemonSet ensures one pod runs on each node. Updating a DaemonSet creates a new revision. If the new pods fail readiness or crash, you can undo the update. Kubernetes stores revision history in the DaemonSet object. You can revert to any recorded revision.
Why use DaemonSet rollback
Automated updates reduce manual errors but may deploy faulty code or misconfigured containers. A rollback restores the previous revision instantly. It limits downtime and maintains stability across nodes. You avoid manual edits on each node.
Prerequisites for DaemonSet rollback
- A Kubernetes cluster with at least two worker nodes.
kubectlconfigured to communicate with the cluster.- An existing DaemonSet with at least two revisions recorded.
- Proper RBAC permissions to view and update DaemonSets.
DaemonSet rollback steps
Follow these commands to revert your DaemonSet:
# Inspect current DaemonSets and revisions
kubectl get daemonset nginx-ds
kubectl rollout history daemonset/nginx-ds
You will see an output similar to:
REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
1 Initial creation
2 Updated image to nginx:1.19
To rollback to revision 1:
kubectl rollout undo daemonset/nginx-ds --to-revision=1
After this, Kubernetes updates pods to match revision 1. New pods will use image nginx:stable if that was the original spec. Pods on each node restart one by one to avoid node disruptions.
Rollback to specific revision
By default, kubectl rollout undo reverts to the previous revision. You can target any recorded revision:
kubectl rollout undo daemonset/nginx-ds --to-revision=
If you omit --to-revision, Kubernetes rolls back one step. Always verify revision numbers before rollback.
Verifying DaemonSet rollback
Check status and events to confirm successful rollback:
kubectl get daemonset nginx-ds -o yaml
kubectl describe daemonset nginx-ds
kubectl rollout status daemonset/nginx-ds
Ensure the .status.collisionCount is zero and the Revision annotation matches the target. Look for UpdatedRevision and CurrentRevision fields.
Troubleshooting DaemonSet rollback
- Pods remain in CrashLoopBackOff: Check container logs with
kubectl logs. Validate image tag and config. - No rollback history: Ensure you did not set
revisionHistoryLimitto zero in the DaemonSet spec. - RBAC error: Grant
updatepermission ondaemonsetsresource to your service account.
DaemonSet rollback workflow
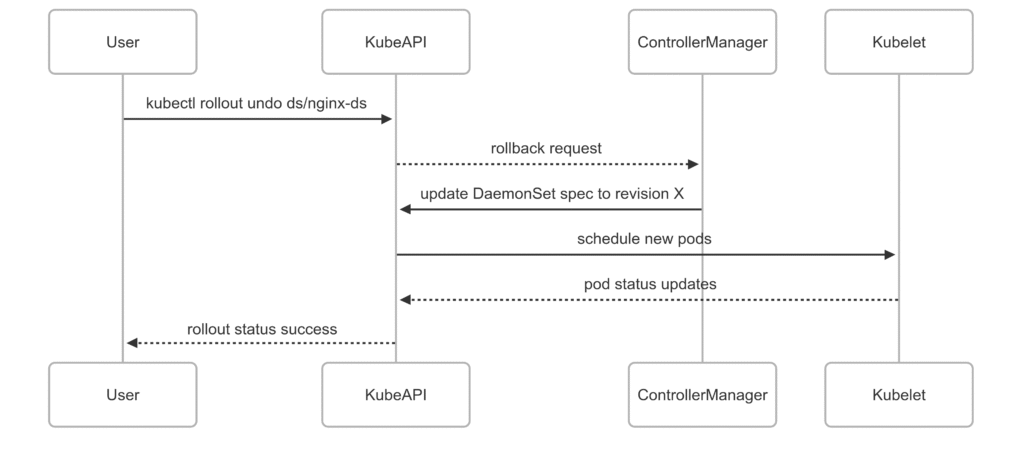
References
Suggested Reading
PostHashID: 63b4a202cbc1182418505264885474da88da98b87b3f5039cf791c30cbcae107




